Advanced digital solutions and key enabling technologies must constantly be reoriented towards solving the problems of the manufacturing sector which can only return to competitiveness by increasing efficiency, reducing time-to-market, minimizing costs and increasing product and service quality.
EnginSoft’s experience confirms the relevant impacts that can be achieved with Digital Manufacturing solutions as predicted by the European Factories of the Future Association:

Digital manufacturing driving business outcomes in detail: Reduced downtime – 48% |
Reduction in defects – 49% | New product introduction – 23% | Overall Equipment Effectiveness improvement –
16% | Improved inventory – 35% | Reduction in energy use – 18%
(Source: European Factories of
the Future Association, www.effra.eu.)
A Digital Twin is a virtual and connected model of a real working system. It reproduces the behavior and history of that system to enable better design, production and operational management of industrial processes, assets, and systems.
EnginSoft proposes various categories of DTs that represent different and distinctive application domains
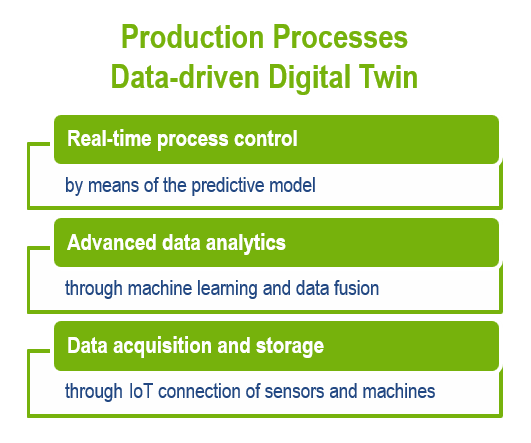
Application of the Digital Twin approach
to advanced and intelligent control
of existing production processes
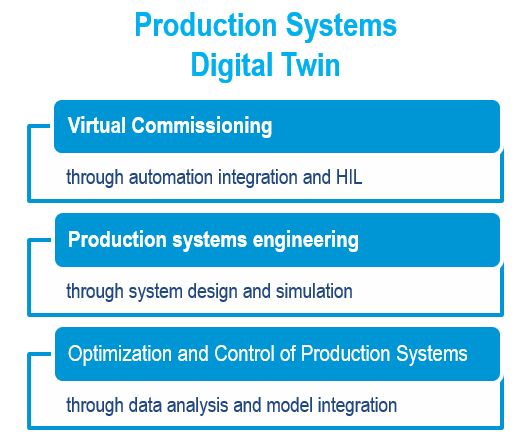
Application of the Digital Twin approach
to production systems
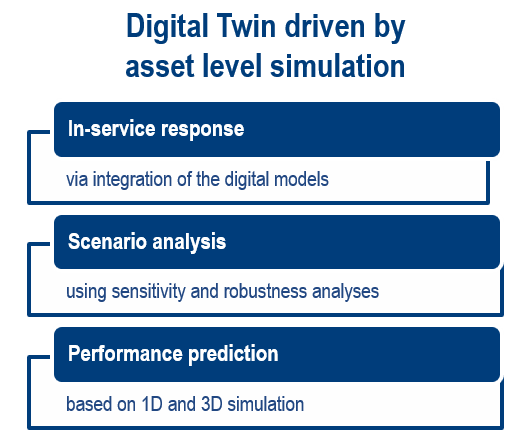
Application of the Digital Twin approach
to Product and maintenance of Production assets
DT consists of three elements: intelligent process control (IPC), AI_driven modelling and Decision Support Systems (DSS)
The combined use of simulation (finite element analysis, FEA) and data analysis reduces costs and increases reliability for quality predictive models.
Using simulation you can understand the production process, identify significant process parameters and the corresponding intervals. Thereafter, you can implement targeted experimental design of experiments (DOEs) and collect the data needed to build the models at a lower cost.
By applying multi-variable analysis techniques you can create accurate predictive models and validate them. The models can then be integrated onto the machine by creating virtual sensors or suggesting the correct process parameters to the operator.
Data-driven Digital Twins:
Designing automatic machines and robotic cells with Virtual Commissioning
Virtual commissioning is applied to the integrated design of mechanics, robotics, and automation of machines, automatic lines, and systems for factory logistics.
The 3D CAD model of the automated machine or production system is used to create a virtual commissioning model, integrating the programming logic of plc and robot controllers, to provide a realistic simulation.
These models allow you to design the system and validate the automation (interaction between sensors, actuators and control software) before its realization, with the aim of simulating its real behavior and preventing problems at the time of commissioning (a "marriage" between the physical machine and the control system). In addition, augmented reality features allow the use of virtual commissioning models to support the sale and maintenance of automatic machines, and for simulation-based training.
Design and optimize systems and production lines with discrete event and agent-based simulation
SIMUL8 is a simulation software for modeling, analyzing and optimizing the system-level performance of production systems during their design, reconfiguration, and production planning phases.
The simulation building blocks allow you to create accurate system models of complex system architectures, such as production lines, job shops, robotics cells, assembly systems and complex product flows. Creating a preliminary model requires limited information (for example starting from a process list and the 2D layout of the plant), while it is possible to progressively add detail to the simulation.
SIMUL8 models provide decision makers with critical information, such as:
The models can be easily connected to optimization algorithms by considering the output objectives (throughput, quality yield), and constraints (machine capacities, failure rates, shift patterns, and other factors affecting the total performance and efficiency of production systems).
Therefore, they allow you to evaluate the effects of different scheduling policies, batch and production flow management and operators, maintenance policies, the impact of system modification interventions (modification of the layout, replacement of machinery, interventions aimed at reducing the average return time of certain events, etc.), the effect of adding new products online, etc. and to identify the best compromise solutions in the face of conflicting objectives (e.g. costs vs. productivity).
Develop asset-level condition monitoring and predictive maintenance models
The combination of technologies for numerical and symbolic calculation (Maple) and a multi-domain simulation systems based on Modelica (MapleSim), allows you to create efficient simulation models that integrate mechanical, electrical, hydraulic, etc. components and their controls. Based on the ability to import 3D CAD models it is possible to accurately model articulated systems (kinematic chains) taking into account masses and inertia. The combination of these features enables accurate modeling that emulates the behavior of real systems.
The efficient generation of C code according to the functional mockup interface (FMI) standard allows you to export the models in the form of a functional mockup unit (FMU) and to support both model exchange and co-simulation by integrating other technologies. The resulting models can be integrated into the machine in the logic using software in the loop (SIL) by creating a digital twin for asset condition monitoring and predictive maintenance.

CASE STUDY
This study was part of the Virtual Optimization PAsta production process (OPAV) research project,
modefrontier ansys ls-dyna magma optimization food-beverage consumer-goods
CASE STUDY
In this technical article, Fiat Chrysler Automobiles explain how they created a multibody optimization project to identify the optimal values for the powertrain suspension stiffness for a three-cylinder engine in order to minimize the vibrations at idle condition and ensuring greater ride comfort to the passengers.
automotive optimization modefrontier
CASE STUDY
The text discusses the importance of digital simulation models in modern factory design and reconfiguration, particularly in response to shorter product lifecycles and increased customization demands. Traditional design methods often lead to inefficiencies and high costs, making digital simulation essential for creating flexible and adaptable production systems. The article highlights a case study involving a furniture assembly factory, where a manufacturer needed to efficiently handle a variety of custom kitchen cabinet orders. The system integrator was tasked with designing a robotic assembly line that could maintain production efficiency despite the high variety of products.
industry4 SIMUL8
Some software solutions for Industry 4.0 - EnginSoft’s approach to Digital Manufacturing
software
Maple is an advanced numeric and symbolic solution with a powerful maths engine. Maple is used by Design Engineers and Advanced Analysts to quickly and accurately perform calculations and mathematical manipulations using live mathematical expressions.
maple maplesim

software
Maple Flow is an advanced software for symbolic processing, visualization, and analysis of mathematical data and models. Developed by Maplesoft, Maple Flow combines the power of symbolic computation with an intuitive interface, allowing users to explore and solve complex problems efficiently.
maple maplesim
software
industrialPhysics is an innovative simulation platform for the digital design and virtual commissioning of complex production machines, lines and plants.
iphysics industry4 optimization mechanics