iPhysics
Digital engineering, simulation and augmented reality for machines, production lines design and plant logistics
ilPhysics is a product of Machineering Gmbh.
ilPhysics is a product of Machineering Gmbh.
iPhysics is an innovative simulation platform for the digital design and virtual commissioning of complex production machines, lines and plants. By integrating the mechanical, electrical and software engineering it provides substantial benefits, such as the possibility to further optimize the machine sequence planning, immediately verify solutions and reduce costs.
iPhysics enables comprehensive engineering from the CAD level to the PLC and robots simulation. It provides the ability to realistically simulate lines and plants and obtain better Throughput and OEE estimates. It enhances communication between the mechanical and the automation design teams effectively reducing risk for complex plants and projects and simplifying commissioning. It provides the possibility to evaluate multiple design solutions and seamlessly explore new ideas and what-if scenarios. Furthermore, industrialPhysics integrates the Augmented Reality features that advance the production processes visualization allowing to effectively engage the design and sales teams with customers.

A collection of videos, which show some applications of this innovative platform for the design and simulation of machines, lines and production plants.
Visit the dedicated area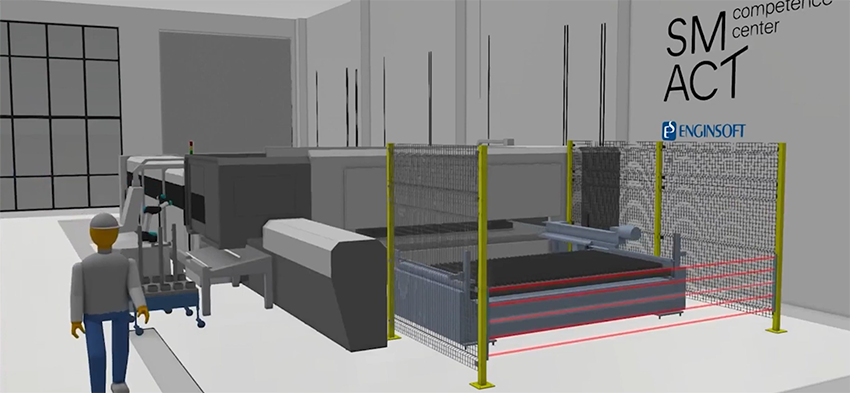

Send your technical questions to our experts!
Connect you with an EnginSoft expert who can provide a reliable answer to your technical question or recommend a
proven solution.

CASE STUDY
This technical article details the application of the methodology developed using ANSYS WorkBench
ansys mechanics maplesim

CASE STUDY
In this case study, EnginSoft engineers explain how they used modeFRONTIER to assist Comau, a Fiat Chrysler subsidiary, to optimize their approach to the preliminary design of production systems for automotive manufacturing system RFQs.
automotive optimization rail-transport modefrontier SIMUL8 iphysics industry4
CASE STUDY
Mesh morphing has proven to be a valuable tool in parametrizing numerical models to perform shape optimization. It allows engineers to save time in generating new configurations for analysis because it does not require geometry modification and mesh re-generation.
ansys mechanics
CASE STUDY
Multibody simulation is integral to engineering, enabling precise analysis of structural loads and dynamic behaviours in complex systems. In the context of forklifts, where tyres play a critical role due to the absence of suspension systems, accurate tyre modelling is essential. This study develops and validates a hysteretic Bouc-Wen model for the radial dynamics of solid rubber tyres to enhance simulation reliability.
multibody recurdyn mechanics automotive

CASE STUDY
This paper presents the RENAULT F1 Team’s AM process for an aerodynamic insert in titanium Ti6Al4V. Production was optimized by identifying the best orientation for the parts and the best positioning for the support structures in the melting chamber, in addition to using the ANSYS Additive Print module, a simulation software useful for predicting the distortion of a part and for developing a new, 3D, compensated model that guarantees the best “as-built” quality.
automotive additive-manufacturing optimization