ViveLab Ergo
Ergonomic verification in 3D virtual space
ViveLab Ergo is a product of ViveLab Ergo Ltd.
ViveLab Ergo is a product of ViveLab Ergo Ltd.
ViveLab Ergo is a high-performance cloud computing innovative simulation system that is perfectly capable of modeling machines, robots and people moving in a given physical environment. Harmonizing the co-operation of these three elements in the industry's 4.0 era is an indispensable task. Using an anthropometric database containing millions of samples, it precisely models ninety-nine percent of human population's anthropometrical characteristics. It highlights the health-damaging effects of forced movements caused by incorrect workplace design using 7 built-in ergonomic analyzes: RULA, OWAS, NASA-OBI, ISO 11226, EN 1005-4, reachability zone, spaghetti diagram.
This technology can be used to ergonomic improvement of existing workstations, ergonomic design of new workstations, or ergonomic design of products. The user-friendly interface has been designed considering the most modern ergonomic viewpoints, which ensures that design engineers, work safety managers, HR specialists, or even creative designers can independently run or collaboration a team to run and evaluate simulations logging in from anywhere in the world.



Send your technical questions to our experts!
Connect you with an EnginSoft expert who can provide a reliable answer to your technical question or recommend a
proven solution.
CASE STUDY
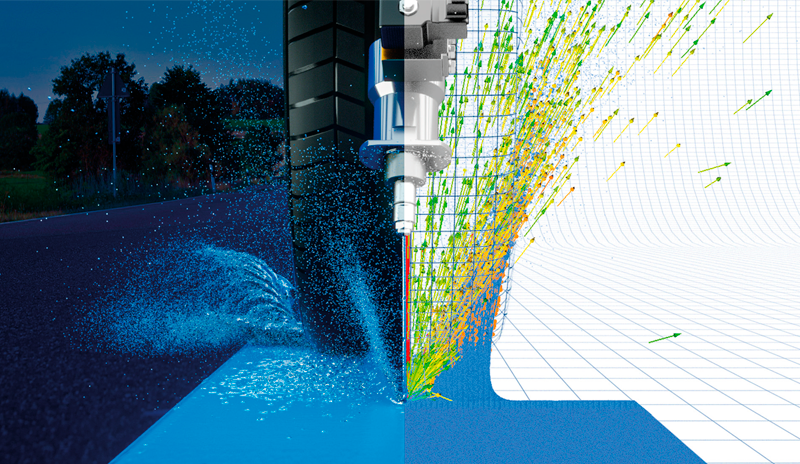
In this paper, we discuss the digital modelling and simulation of the EASYRAIN Aquaplaning Intelligent Solution (AIS) using mesh-free moving particle simulation (MPS).
automotive particleworks
CASE STUDY
This study by Hitachi Rail investigates how various designs of energy absorbers perform under offset collision conditions in railway vehicles. Using finite element simulations (240 in total), the research explores different absorber geometries—such as thin-walled multi-cell and bi-tubular structures—and analyses how factors like thickness, shape, and cross-sectional dimensions affect energy dissipation.
automotive rail-transport
Our competences in ViveLab Ergo
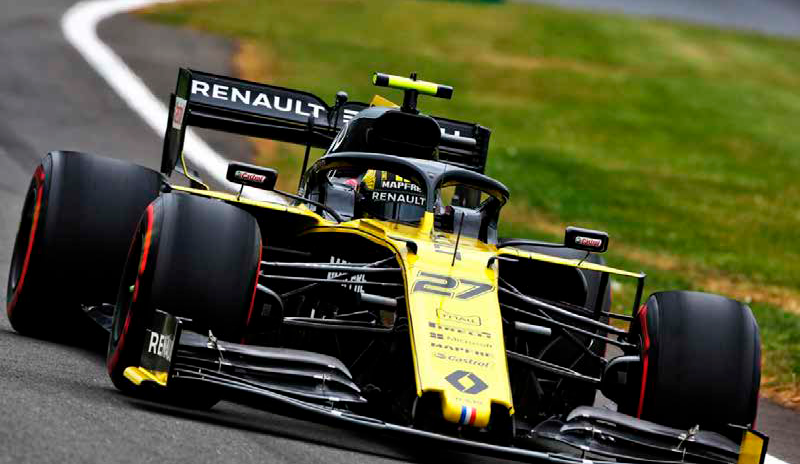

CASE STUDY
This paper presents the RENAULT F1 Team’s AM process for an aerodynamic insert in titanium Ti6Al4V. Production was optimized by identifying the best orientation for the parts and the best positioning for the support structures in the melting chamber, in addition to using the ANSYS Additive Print module, a simulation software useful for predicting the distortion of a part and for developing a new, 3D, compensated model that guarantees the best “as-built” quality.
automotive additive-manufacturing optimization
CASE STUDY
In this article, Del Negro explains how Ricardo is developing solutions to support its customers to predict the lifecycle of motorcycle components, using finite element analysis (FEA) and fatigue analysis.
femfat mechanics automotive

CASE STUDY
This study presents the work undertaken by Dana Incorporated to develop a new independent suspension axle for an off-highway vehicle (OHV). This multi-disciplinary simulation activity combines improvements to the kinematic and dynamic performance of the suspension while also examining the constraints of the mechanical design and the hydraulic system, as well as the cost of the suspension.
modefrontier automotive

CASE STUDY
The barrier has been thoroughly tested and certified against car and bus impact conditions.
automotive ls-dyna
CASE STUDY
The article discusses advancements in low cycle fatigue analysis for an electric motor's rotor, focusing on a new method implemented in the FEMFAT software. Traditional methods have limitations in accurately predicting material plasticization due to a lack of consideration for the sequence of load peaks, which can affect component lifespan.
automotive femfat
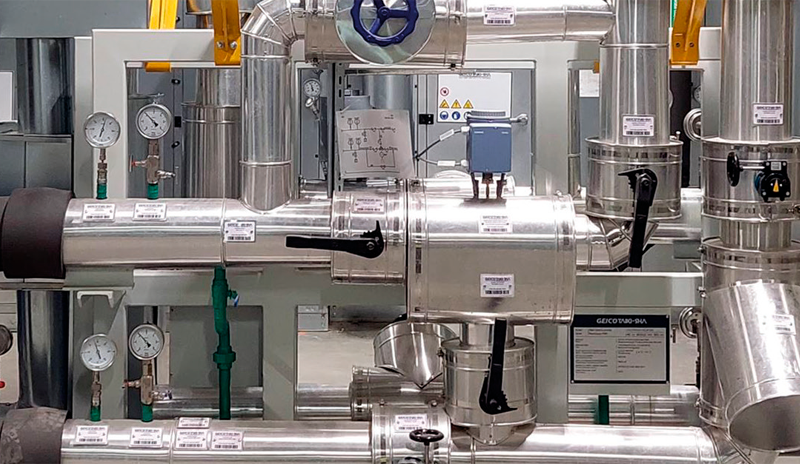

CASE STUDY
This article describes an analysis of the performance of a hot water distribution piping network consisting of a main boiler and various utilities inside an automotive paint shop based in France. The simulation is performed using Flownex, a CFD (computational fluid dynamics) software with concentrated parameters.
automotive flownex

CASE STUDY
Understanding the flow of oil lubrication in transmissions and axles is vital to improving their efficiency and reducing the wear of key components. The choice, and volume of lubricant, and the shape of the gearbox housing can all be optimized for the expected gear speeds, loads, and temperatures.
automotive particleworks

CASE STUDY
This article combines the use of the finite element method with a Design Thinking approach to reconstruct a road traffic accident for an traffic accident insurance report in order to analyse the outcome of the accident, compare the respective property damage, and the physical injuries to pedestrians or passengers in order to limit the quantity of large claims compensation for the insurance company, while ensuring the fairness of the compensation for the customer to foster greater trust and credibility in the insurance provider.
automotive ls-dyna

CASE STUDY
RecurDyn software allows belt-type systems, including CVTs, to be both modelled and simulated accurately. The dedicated “Belt Toolkit”, which is an automated modeling assistant, includes all of the components found in a belt-type transmission.
automotive rail-transport recurdyn
CASE STUDY
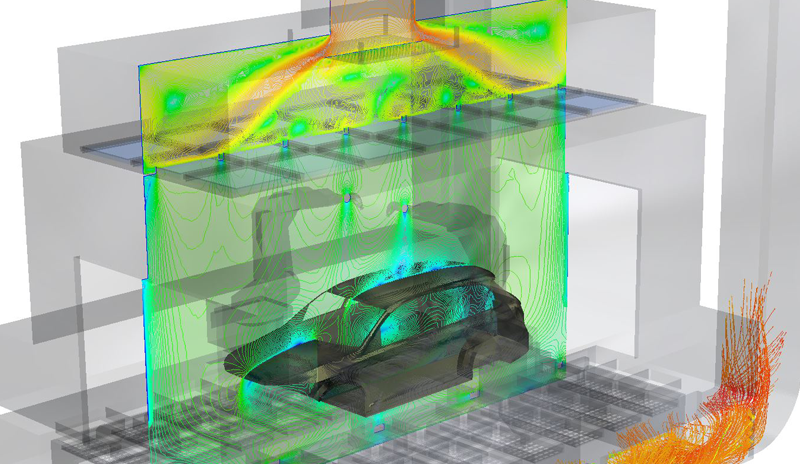
Overspray is a key problem in the paint application process. This phenomenon is caused by inefficiencies of the robots inside the spray booth and can best be solved by balancing the air flow properly in the paint application area.
automotive ansys cfd
CASE STUDY
This article discusses the use of moving particle simulation of the oil distribution system to predict heat dissipation and temperature distribution in the engine in order to examine virtual e-drive prototypes to improve their final design.
particleworks automotive
CASE STUDY
This article presents the challenges of conducting fatigue analysis on rubber components due to their nonlinear behaviour, contrasting this with linear superposition methods used in metal fatigue analysis. Traditional linear methods are effective for linear materials, allowing for efficient stress-strain history generation through the scaling of finite element (FE) solutions based on input load histories. However, these methods fail for rubber because of its complex material properties and behaviours.
endurica automotive
CASE STUDY
Thermal management (TM) is a critical challenge in developing efficient, compact, and reliable electrified products in the automotive industry and beyond. TM encompasses strategies and technologies that maintain optimal operating temperatures for system components, ensuring safety and efficiency. This study explores TM in electrified products, focusing on the integration of hydraulic units, electric motors, and electronics, and the importance of system-level design from the pre-design phase.
automotive cfd
CASE STUDY
The article focuses on the increasing importance of simulation in product development, particularly for vehicles, to identify potential issues early and reduce costs associated with design changes. As physical prototypes become more expensive to modify, integrating virtual testing allows for the assessment of design parameters and product performance before mass production.
automotive
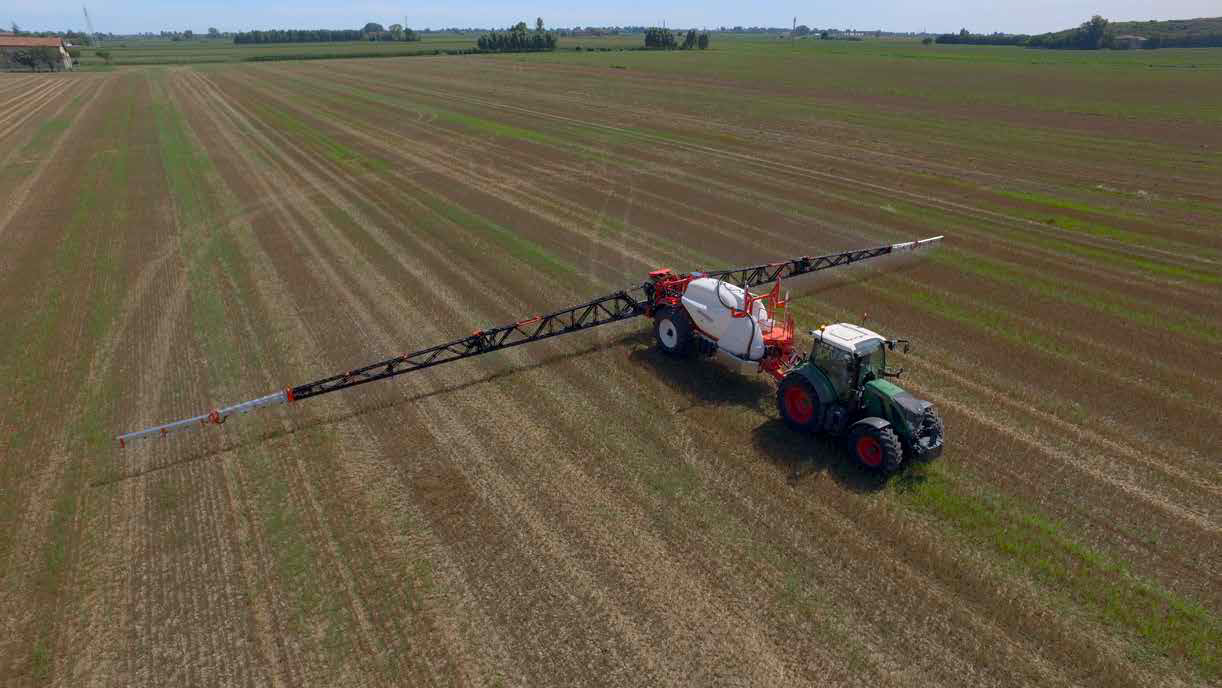

CASE STUDY
This case study describes how the company’s R&D team used ANYSYS and Spaceclaim to conduct Finite Element Method analyses to refine the design of a new model of a sprayer boom used by farmers to distribute phytosanitary products over fields for crop protection.
ansys automotive rail-transport
CASE STUDY
The study described in this article was designed to obtain greater insight into the gas transfer mechanism at microscopic scale using computational fluid dynamics in order to accelerate design exploration to find the optimal solution.
biomechanics ansys
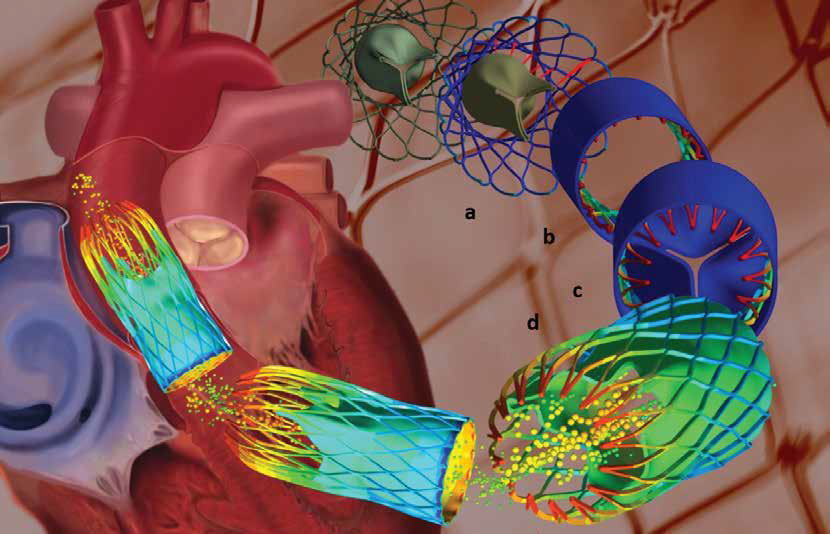
CASE STUDY
Since this cannot be accurately measured in an implanted stent, manufacturers decided to use Multiphysics to simulate the process to better understand the method and to calculate the forces operating on the implant in order to improve the stent design and the surgical procedure, as described in this article.
cfd biomechanics ansys
CASE STUDY
This article describes a new method of aerodynamic design, the result of a collaboration between Dallara Automobili and RBF Morph, that uses adjoint methods and mesh morphing to create an innovative solution to accelerate the optimization process, reducing both time and costs.
automotive rbf-morph

CASE STUDY
This technical article describes how high-end numerical Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations were applied to mimic the realistic operating conditions of a Ventricular Assist Device (VADs) and analyze its hemodynamics in order to identify potential areas for optimization of the device’s performance, safety and efficacy.
ansys cfd biomechanics

CASE STUDY
Futurities interviewed Paul Stewart about his thoughts on the evolution of simulation’s role in the design process in the automotive industry, the evolving roles of CAD and CAE and the move to freeform deformation in automotive design, as well as the likely impact and role of artificial intelligence technologies in this space.
automotive

CASE STUDY
This brief article summarises how California-based electric car company, Lucid Motors, used the CAE application, ModeFRONTIER for performing Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
automotive optimization modefrontier

CASE STUDY
The car is designed to race on the ultra-flat Salt Flats in Bonneville, Utah. The racecar weighs less than 500kg so increasing the downforce was critical. Reducing aerodynamic drag was also critical due to the power requirements of the racecar.
cfd automotive
CASE STUDY
This technical article describes a project that was undertaken by TAE SUNG Software and Engineering, in collaboration with DY AUTO in Korea, to establish a computerized process to conduct three-dimensional real-scale analysis of any of the three types of windshield wiper currently in use, and to establish a specific standard for evaluating wiper performance.
automotive ls-dyna ansys
CASE STUDY
This article discusses a realistic multi-objective parameter optimization study of a highly athletic one-legged robot, called Skippy, in which both the parameters of the mechanism and the parameters of its optimal behaviors were sought.
optimization modefrontier biomechanics
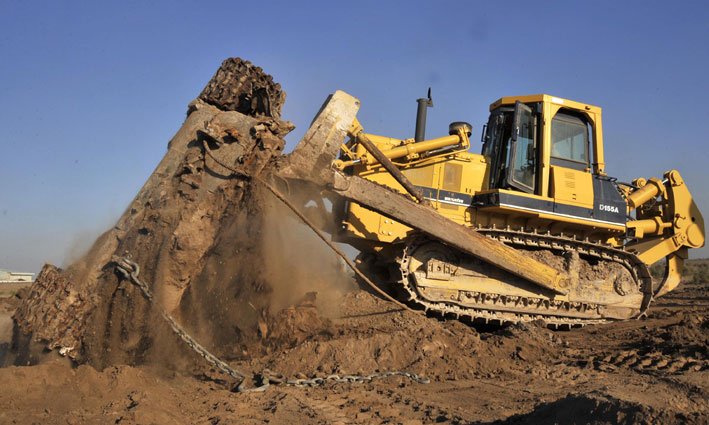

CASE STUDY
In this example, a tracked bulldozer was simulated to evaluate the dynamic behavior of the vehicle on different terrains and with different obstacles. The model can also be used to calculate the loads operating on the vehicle’s structure..
recurdyn automotive mechanics multibody
CASE STUDY
The article focuses on the difference in fatigue behaviour between rubber and metal materials. While metal fatigue is often described by a simple rule: increasing mean strain is detrimental to fatigue life, rubber fatigue is more complex and depends on the material's ability to strain crystallize. The text concludes that while tensile mean stresses are always detrimental in metals, in rubber they may be either beneficial or harmful depending on whether the rubber can strain crystallize.
mechanics endurica automotive
CASE STUDY
This article introduces a case study on the waterproofing of an automotive air conditioning system for rainy conditions using Particleworks, a particle method CFD software.
particleworks automotive

CASE STUDY
In this technical article, we demonstrate how to apply a one-way coupling technique using a combination of ParticleWorks and LS-DYNA to estimate tsunami damage to a vehicle.
automotive ls-dyna energy cfd particleworks environmental

CASE STUDY
Dynamic studies are required to predict the accelerations, verify that the cams are properly shaped, and to extract the loads to structurally size the parts.
recurdyn multibody mbd-ansys automotive

CASE STUDY
This type of highly-defined model provides valuable outputs: the contact analysis provides detailed information about the pressure and friction between the parts, which is useful for estimating wear
automotive multibody recurdyn

CASE STUDY
ptimization of the product starts with a strong correlation of the model with specifically designed tests under controlled conditions.
ansys automotive
CASE STUDY
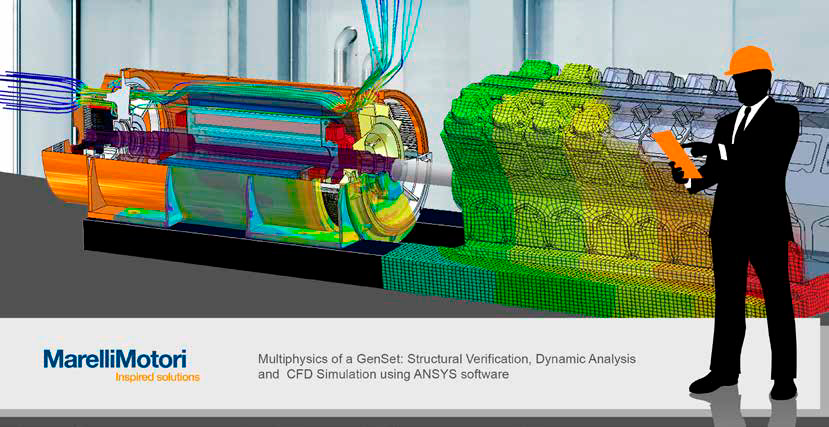
Marelli Motori engineers use Ansys multiphysics solutions to custom-design motors and generators to solve challenges in hydropower, cogeneration, oil and gas, civil and commercial marine transport, military applications, and ATEX applications involving motors and generators in explosive atmospheres, among other applications.
automotive ansys energy
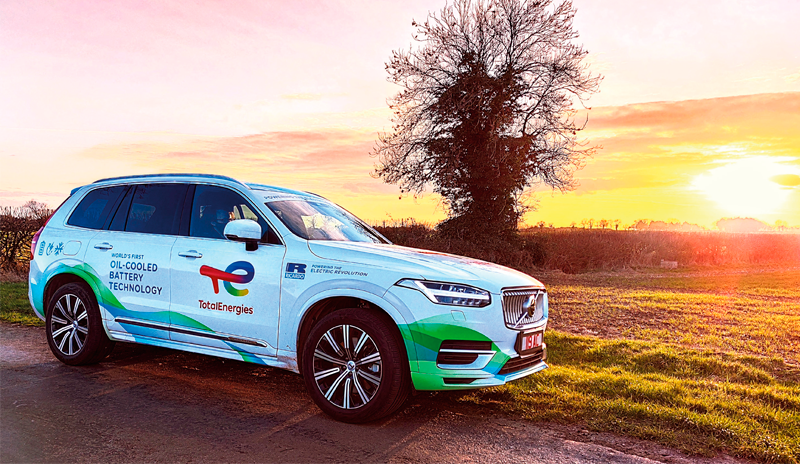

CASE STUDY
In this paper, we will present the methodology developed by TotalEnergies and EnginSoft to select, design and improve an e-motor by simulating and predicting electromagnetic losses, fluid flow behaviour and temperature distributions.
automotive electronics particleworks
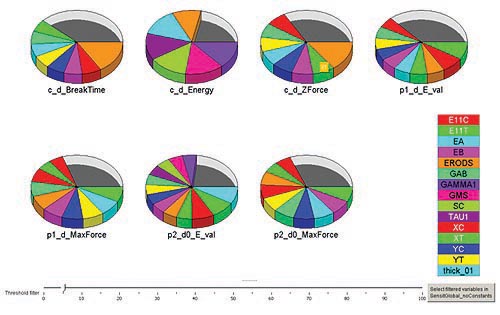
CASE STUDY
While the engineers relied on modeFRONTIER's capabilities, the procedure has been to calibrate the constitutive parameters of LS-DYNA's advanced material models, and to use them for prediction, design optimization and robustness analysis.
modefrontier ls-dyna automotive composites
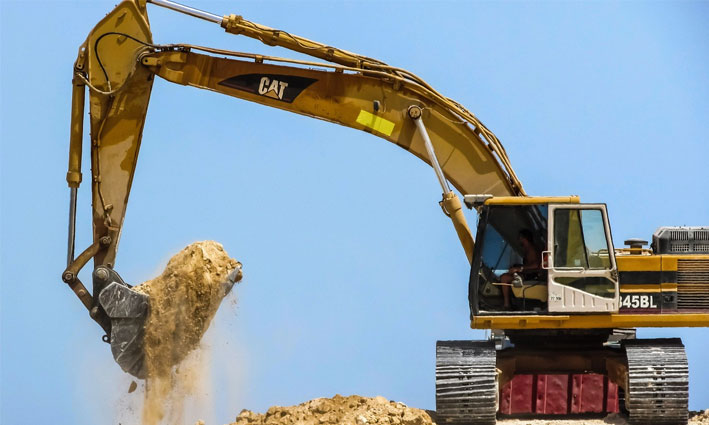

CASE STUDY
A multibody model of an excavator was developed to calculate the loads acting on the structure and to perform static structural verifications of the different components.
automotive multibody recurdyn mechanics
CASE STUDY
This paper demonstrates how the biological growth method, studied by Mattheck in the 1990s, can be easily implemented for structural shape optimization finite element method (FEM) analyses using advanced radial basis functions (RBF) mesh morphing.
ansys biomechanics rbf-morph
CASE STUDY
This paper presents the main steps taken in the development phase of the IVECO cab suspension brackets to comply with the new ECE R29 crash regulation for Heavy Commercial Vehicles (HVC).
modefrontier optimization automotive
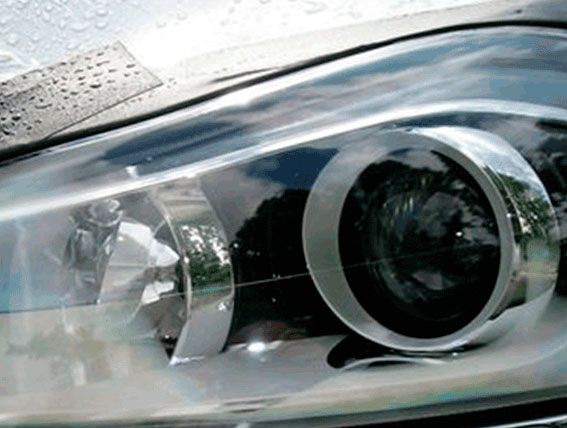

CASE STUDY
EnginSoft implemented a new 3D CFD multi-phase model to simulate the water condensation-evaporation processes inside automotive headlamps for Automotive Lighting, a leading supplier of quality headlights to the OEM market
automotive cfd ansys rail-transport

CASE STUDY
In this paper, we discuss the digital modelling and simulation of the EASYRAIN Aquaplaning Intelligent Solution (AIS) using mesh-free moving particle simulation (MPS).
automotive particleworks
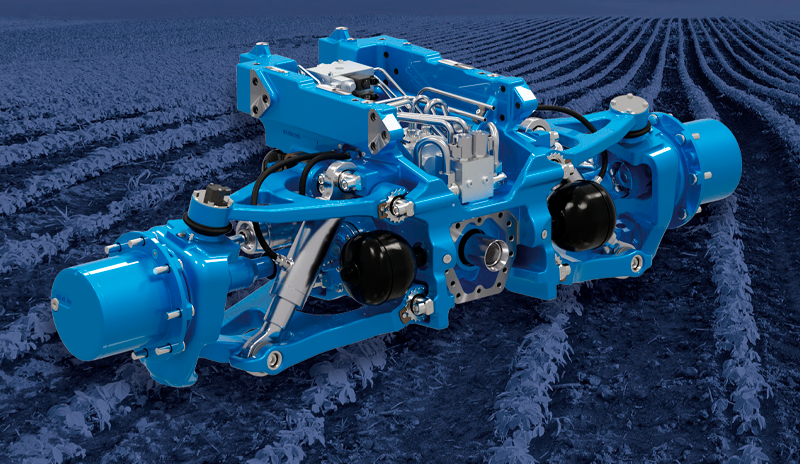
CASE STUDY
The purpose of the case study was to implement a design methodology that used multi-disciplinary simulation and an automated process to analyse thousands of product configurations and highlight vehicle performance distributions in terms of handling, comfort, and cost. This approach ensures that the best solution is always selected.
mechanics modefrontier automotive optimization
CASE STUDY
This article provides a non-exhaustive overview of some of the latest advances in the adoption of CAE technologies in the medical field by citing some ongoing EU research programs.
rbf-morph biomechanics
CASE STUDY
Motorsport’s competitive demands drive innovation, such as optimizing fuel tank performance by reducing sloshing and ensuring efficient fuel extraction. This study explores a meshless CFD approach using Moving Particle Simulation (MPS) to streamline workflows and reduce computational costs compared to traditional finite volume method (FVM) CFD.
automotive cfd particleworks
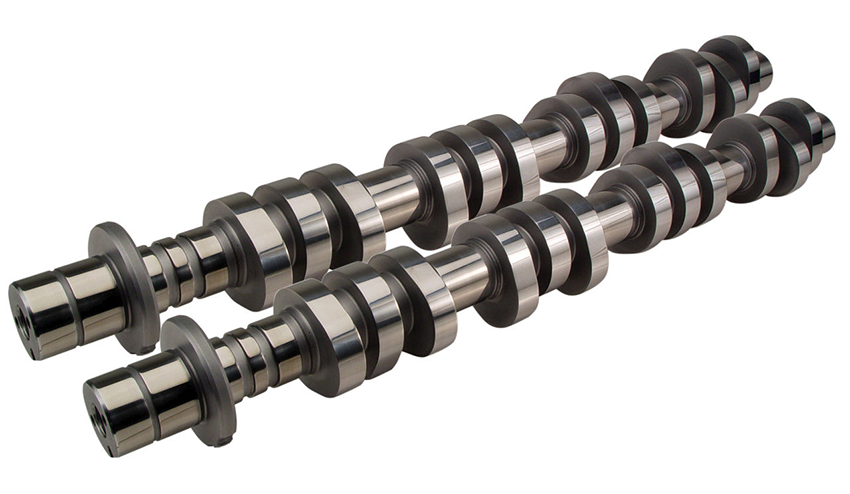

CASE STUDY
This technical case study explains the application of a two-step methodology using the MATLAB and Adam algorithms in the modeFRONTIER software platform.
optimization modefrontier automotive
CASE STUDY
Transmission design is mainly based on the mechanical aspects of the transmission and lubrication is an aspect that is verified, and eventually corrected, based on bench testing, i.e. once the design phase has been completed and a physical prototype is available.
mechanics particleworks automotive
CASE STUDY
Multibody simulation is integral to engineering, enabling precise analysis of structural loads and dynamic behaviours in complex systems. In the context of forklifts, where tyres play a critical role due to the absence of suspension systems, accurate tyre modelling is essential. This study develops and validates a hysteretic Bouc-Wen model for the radial dynamics of solid rubber tyres to enhance simulation reliability.
multibody recurdyn mechanics automotive

CASE STUDY
This detailed technical case study describes how the students arrived at a supersonic aircraft drone prototype using MATLAB and modeFRONTIER in order to reduce the time and costs of numerical and wind-tunnel testing.
automotive modefrontier optimization
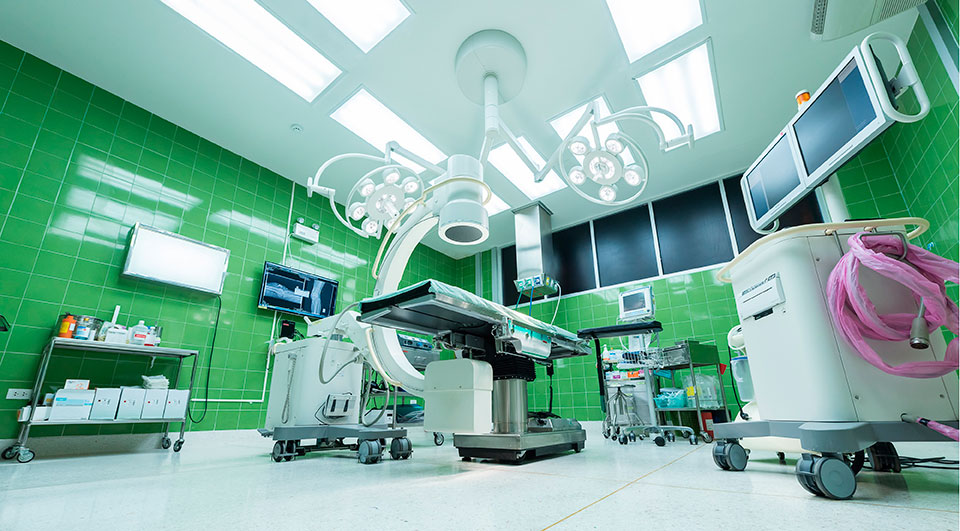
CASE STUDY
Further reduction of the heat loss compared to the best design of the NSGA-II first phase design optimization: a further 4% gained
cfd biomechanics ansys modefrontier optimization
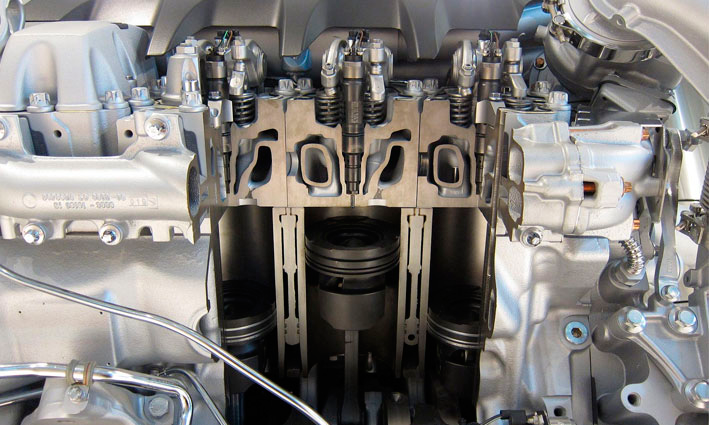
CASE STUDY
The model contains both rigid and flexible bodies: the pin was modelled using the proprietary Full Flex technology which includes a Finite Element body in the dynamic simulation.
recurdyn mbd-ansys automotive multibody
CASE STUDY
In this technical article, Fiat Chrysler Automobiles explain how they created a multibody optimization project to identify the optimal values for the powertrain suspension stiffness for a three-cylinder engine in order to minimize the vibrations at idle condition and ensuring greater ride comfort to the passengers.
automotive optimization modefrontier

CASE STUDY
The connecting rod is one of the most important components in powertrain systems, so it requires very careful structural analyses because its failure implies serious damage to the entire engine.
automotive ansys rail-transport
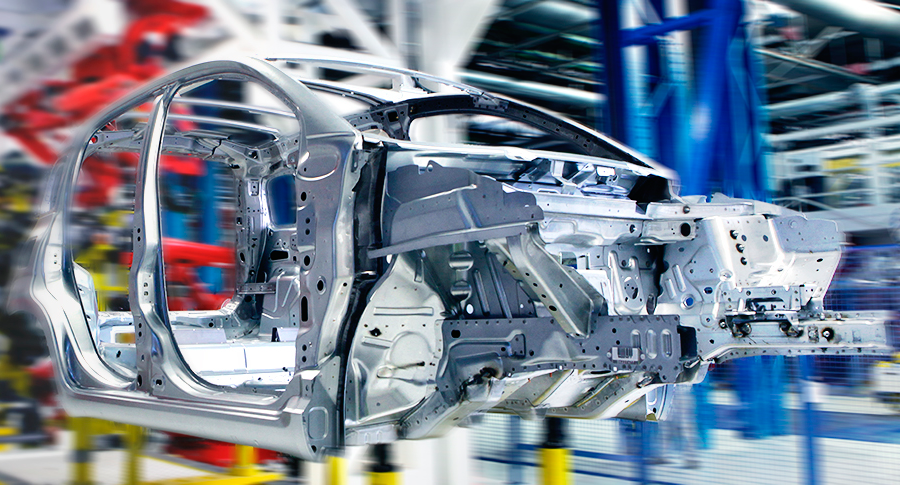

CASE STUDY
In this case study, EnginSoft engineers explain how they used modeFRONTIER to assist Comau, a Fiat Chrysler subsidiary, to optimize their approach to the preliminary design of production systems for automotive manufacturing system RFQs.
automotive optimization rail-transport modefrontier SIMUL8 iphysics industry4
CASE STUDY
In this article, we describe how Piaggio used computer-assisted engineering simulation to evaluate the structural safety, performance and dynamic behavior of the driving mechanism of a two-wheeled vehicle under both normal and spurious operating conditions, specifically static and fast dynamic conditions.
automotive multibody
CASE STUDY
Off-road vehicles are evolving towards full sustainability, driving the need for solutions that maximize fuel efficiency while reducing atmospheric emissions. To meet the growing interest in electrification, the significant challenge of power loss management in electric engines must be addressed.
particleworks automotive

CASE STUDY
Particle-based CFD (computational fluid dynamics) methods have become very popular in recent years due to the simplicity of the model configuration process and the ability to solve free surface problems such as splashing.
automotive particleworks
CASE STUDY
This article presents an example of a proposed design optimization approach with a case study.
biomechanics modefrontier

CASE STUDY
A new methodology is presented, following an integrated process-product analysis approach, showing some benefits related to increased accuracy and the potential application of new optimization methods.
ls-dyna automotive composites
CASE STUDY
Improving efficiency while reducing cost is a very complex engineering challenge. Marelli Motori makes extensive use of CFD and FEM multiphysics simulation to do just that in the design of its electrical motors and generators.
ansys automotive cfd
CASE STUDY
This technical article presents a simulation process to analyze fatigue in electronic parts, particularly in solder joints, on printed circuit boards (PCBs).
femfat electronics automotive

CASE STUDY
This article describes how EnginSoft supported Metasystem in acquiring the know-how to satisfy future customer requests on the one hand, and to create projects that are as profitable as possible in terms of waste minimization, on the other hand.
automotive tolerances cetol

CASE STUDY
A client wanted to evaluate the dynamic performance of a new-concept forklift, so a fully-functional multibody model of the forklift was built by assembling the client’s CAD geometries.
multibody automotive mechanics recurdyn
CASE STUDY
This study by Hitachi Rail investigates how various designs of energy absorbers perform under offset collision conditions in railway vehicles. Using finite element simulations (240 in total), the research explores different absorber geometries—such as thin-walled multi-cell and bi-tubular structures—and analyses how factors like thickness, shape, and cross-sectional dimensions affect energy dissipation.
automotive rail-transport

CASE STUDY
This technical article describes a human body model (HBM) wizard developed for RecurDyn and discusses what is already possible and what is in the development pipeline for the near future. Biomotion Solutions provides software to quickly build HBMs in industrial-grade simulation packages.
multibody recurdyn industry4 biomechanics
CASE STUDY
In this technical article, a CFD study of various designs for four different specialty tractors: two brands of specialty tractors for vineyard configurations, and two brands of specialty tractors for orchard configurations, are described.
automotive ansys cfd

CASE STUDY
In this technical article, EnginSoft and Prometech explain how they executed a highly complex computational simulation on the fluid-structure interaction of the oil flow inside a reciprocating engine, on behalf of Honda R&D.
automotive cfd particleworks
CASE STUDY
The article discusses the importance of understanding the behaviour and performance of batteries under different operating conditions, particularly in the context of large-scale adoption of batteries. The hybrid approach has successfully identified the Goldilocks Zone for electrochemical parameters and provides a good match between predicted and experimental data.
automotive oorja energy

CASE STUDY
This technical case study describes how the ROPS and FOPS of a tractor were numerically studied in the early design phase to ensure compliance with OECD Standard Code 4 (for the cabin’s resistance to longitudinal, lateral and vertical energy or force) and Code 10 (for overhead protection from falling objects).
automotive rail-transport ls-dyna