RLW Navigator
Remote Laser Welding Navigator


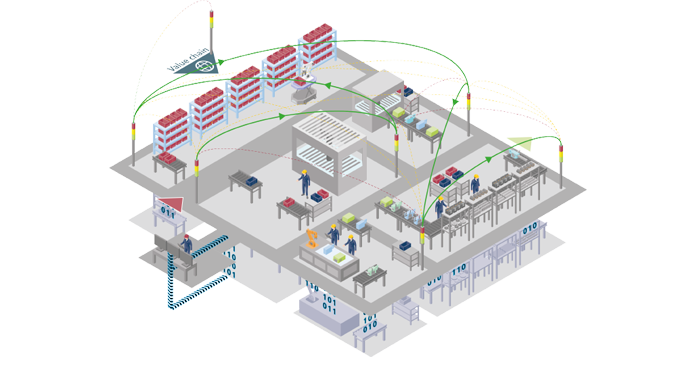
Smart manufacturing - Automotive Production Assembly Line
To develop an innovative Process Navigator to configure, integrate, test and validate applications of Remote Laser Welding (RLW) in automotive assembly line
RLW is emerging as a promising joining technology for sheet metal assembly due to benefits on several fronts including reduced processing time, (50-75%) and decreased factory floor footprint (50%), reduced environmental impact through energy use reduction (60%), and providing a flexible process base for future model introduction or product change. Currently, RLW systems are limited in their applicability due to an acute lack of systematic ICT-based simulation methodologies to navigate their efficient application in automotive manufacturing processes. The project aims to address this by developing a Process Navigator simulation system that will deal with three key challenges thereby allowing manufacturers to utilize the advantages of the RLW system.
The most critical obstacle that currently prevents the successful implementation of RLW is the need for tight dimensional control of part-to-part gap during joining operations, essential to ensure the quality of the stitch. The existing assembly system architecture must be reconfigured to provide the opportunity to evaluate the RLW system in terms of its feasibility to perform all required assembly tasks. The project will develop systematic evaluation and learning methods to assess and improve the overall performance, cost-effectiveness and eco-efficiency of the RLW system.
ES will mainly contribute in the integration of the results from the production system level and the work station level by developing the RLW Navigator Architecture and the relative Software Modules Integration Platform. ES will also be involved in the dissemination of project results in and outside the consortium.
The University of Warwick | Magyar tudomanyos akademia szamitastechnikai es automatizalasi kutato intezet | Politecnico di Milano | University of Patras | Ecole polytechnique federale de lausanne | Università degli Studi del Molise | Jaguar Cars Limited | Stadco Automotive Limited | Comau SpA | Precitec KG | EnginSoft SpA | Ulsan national institute of science and technology | Land Rover
Funding Scheme FP7 | Call identifier THEME [FoF-ICT-2011.7.4] [Digital factories: Manufacturing design and product lifecycle management]


3 years
January 2012 – December 2014
University of Warwick | Principal contact: Professor Darek Ceglarek
Antonio Taurisano – Francesco Franchini
14

Some of our competences in research and technology transfer
Research project
The overall objective of the RaRe2 project is to create a flexible and resilient Holistic Ecosystem Platform powered by the interactions of many European organizations interested in cooperating in the rapid reconfiguration of process chains through collaborative systems and adaptive workforce up-skilling.

Research project
The core of this project is the development of a trade-off study, meant to compare several different structures incorporating new technologies, in order to determine the most promising solutions among those considered
Research project
The SIADD project aims to increase the manufacturing quality and sustainability of some additive manufacturing processes for metals, composite materials and multi-material metals/ composites, while also taking into account the personnel’s economic and environmental conditions and well-being.