HPC4POP
High Performance Computing for Performing Optimized Pumps


Machinery (Cloud-Based CFD Optimization of Magnetic Drive Pumps using HPC)
The experiment will investigate and optimize magnetic-drive centrifugal pumps using Cloud-based HPC with the objective of improving performance and developing new products. Mag-drive chemical-process pumps eliminate the need for shaft sealing, increasing safety while reducing costs. Axial thrust balancing is critical for the design: CFD allows this to be predicted, but the optimization of the pumps to maximize efficiency, minimize thrust, and avoid cavitation requires very large models. Thus, advanced HPC infrastructure and CFD engineering tools are essential.
CDR Pompe will provide the necessary specifications to create a model to study the operating conditions of its pumps, aiming at improving their performance and creating a product that better fits the market needs. As these goals require High-Performance Computing (HPC) infrastructure and engineering tools, the simulation will involve high fidelity CFD transient analyses, on ANSYS software. The optimization process will be geometry-related and based on the Design of Experiment (DoE) and Response Surface methodologies. In this regard, EnginSoft has committed to supplying the engineering know-how in terms of CFD modelling, while CINECA will provide the hardware and support needed to conduct CPU-intensive parallel computating through the cloud.
While a single pump impeller can easily be studied, simulated, and optimized, an entire machine is a totally different undertaking. Modelling the full performance curve to revamp the pump design while seeking to maximize efficiency and minimize thrust and cavitation requires a far more complex model. This is particularly challenging because any assumptions made to simplify periodicity fail when applied to the magnetic drive system in a real operating scenario.
This innovative approach aims to operate and test the pumps in extreme and critical situations, such as off-design conditions at the cavitational or vibrational limits: the multi-domain parametric calculation will make it possible to optimize the pump’s performance and working range, thus increasing the expected productivity and reducing the required maintenance.
EnginSoft will take advantage of its extensive experience in the rotating machinery market to supply the engineering know-how in terms of fluid dynamics parameterization and CFD modelling. EnginSoft’s technical activity involves selecting the best turbulence model and rotating frame algorithms to accurately predict the pump’s performance parameters, with a special focus on axial thrust. The parametric geometry will be created guaranteeing the greatest robustness and meshing efficiency, using ANSYS geometric and automatic mesh tools. The CFD solution will be set up to be automated and repeatable for all project designs, with both qualitative and quantitative monitoring of the main results. The automated process will run its hundreds of design points on CINECA’s HPC facility thereby gathering enough data to optimize the pumps using the response surface methodology.
End User: CDR Pompe
Domain Expert: EnginSoft
HPC Provider: CINECA
This experiment has received funding from the European High-Performance Computing Joint Undertaking (JU) through the FF4EuroHPC project under grant agreement No 951745. The JU receives support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme and Germany, Italy, Slovenia, France, Spain.

15 months
March 2022 – May 2023
EnginSoft
Alessandro Arcidiacono
3
by Alessandro Arcidiacono, Marisa Zanotti | EnginSoft
Luigi Fossati | CDR Pompe
Futurities - Autumn 2023
HPC4POP has been successfully completed, obtaining more efficient and optimized magnetic drive pumps, relying on high-fidelity Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations and taking advantage of High Performance computing (HPC) infrastructure.
Read the article
Some of our competences in research and technology transfer
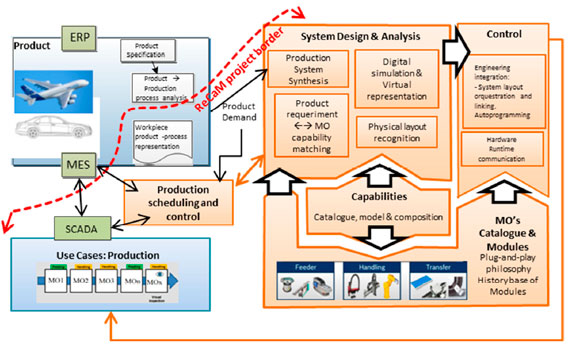
Research project
The ReCaM-project demonstrates at TRL 7 a set of integrated tools for the rapid and autonomous reconfiguration of agile production systems
Research project
The MUSIC is strongly aimed at leading EU-HPDC/PIM factories to cost-based competitive advantage through the necessary transition to a demand-driven industry with lower waste generation, efficiency, robustness and minimum energy consumption.

Research project
The MUSIC is strongly aimed at leading EU-HPDC/PIM factories to cost-based competitive advantage through the necessary transition to a demand-driven industry with lower waste generation, efficiency, robustness and minimum energy consumption.