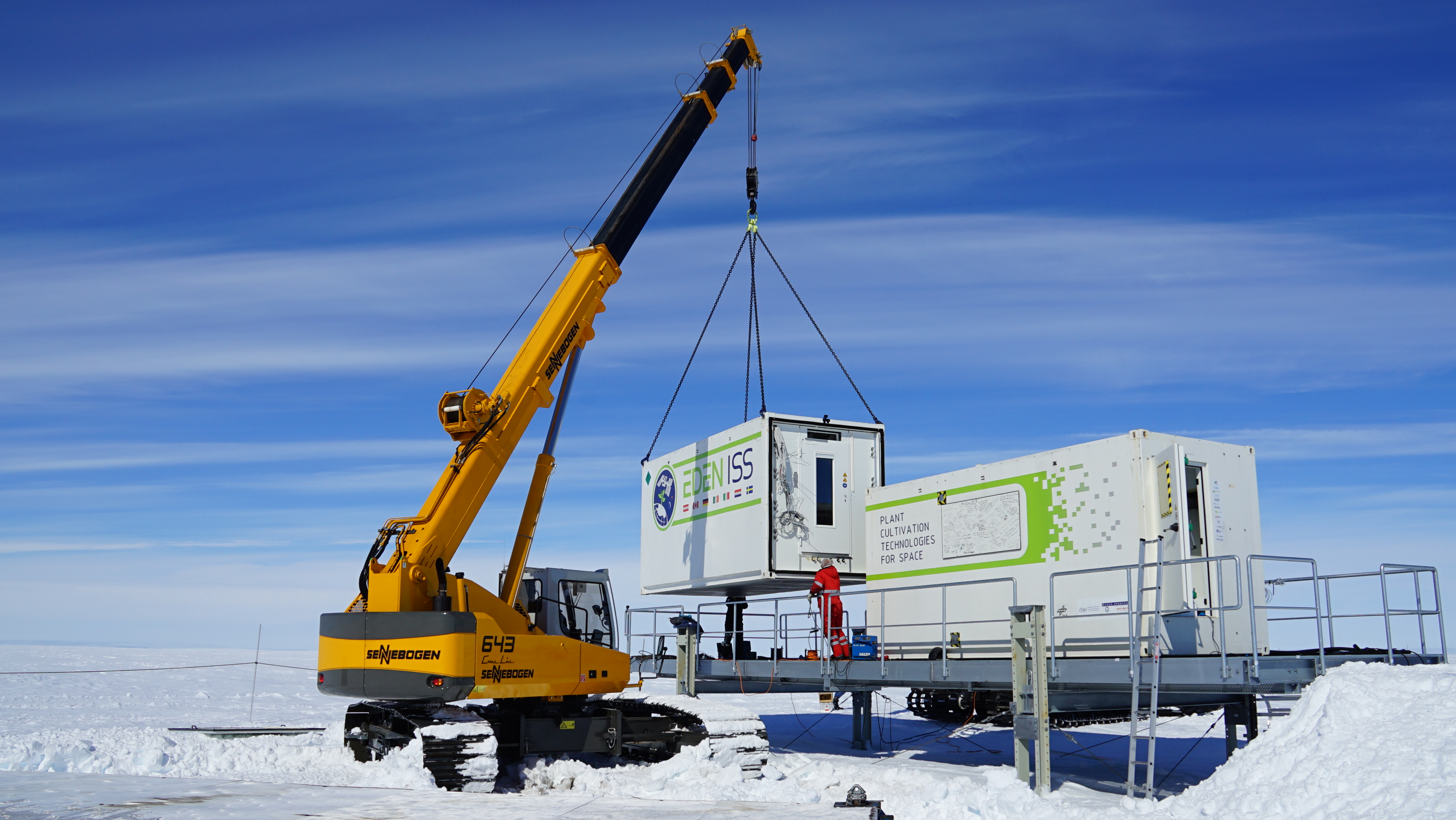
EDEN ISS
Ground Demonstration of Plant Cultivation Technologies and Operation in Space


Space
The aim of EDEN ISS is to identify operation procedures for safe food production in space through adaptation, integration and demonstration of higher plant cultivation techniques.
The basic idea of EDEN ISS is to the develop an ISPR (International Standard Payload Rack)-like system for food production, integrating a controlled agricultural environment characterized by constraints which are analogue to those related to the use of the system in Space and test it on Earth.
EDEN ISS combines the disciplines of plant physiology, biochemistry and mathematical modeling with the design of key electrical and mechanical elements.
The development of an ISPR based higher plants cultivation system with a production area of 1 m2 is ambitious and challenging task. The real-time detection of microbiological contamination and the specific decontamination depending on the type and level on contamination supports the mid-term sustainability of the plants in the green house and represents a substantial step towards a reliable "food production" in orbit.
Participant in the facility design CE-study | Responsible for thermal fluid dynamics and environmental simulations | Performer of detailed CFD simulations of the environmental control
DLR German Aerospace Center, Germany | LIQUIFER Systems Group, Austria | National Research Council, Italy | University of Guelph, Canada | Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research, Germany | Enginsoft S.p.A., Italy | Airbus Defence and Space, Germany | Thales Alenia Space Italia S.p.A., Italy | Arescosmo S.p.A., Italy | Wageningen University and Research, the Netherlands | Heliospectra AB, Sweden | Limerick Institute of Technology, Ireland | Telespazio S.p.A., Italy | University of Florida, USA | Scientific Advisory Board (SAB)

Funding Scheme Horizon2020 | Call identifier H2020-COMPET-7-2014


42 months
March 2015 – September 2018
DLR
Lorenzo Bucchieri
13

Some of our competences in research and technology transfer

Research project
ProRegio project aims at developing a manufacturing intelligence based product-service that can rigorously change the current way customer requirements are addressed by manufacturing companies.
Research project
The scientific and technological objective of the project is to create a hybrid system where a neural network in the brain of a living animal and a silicon neural network of spiking neurons on a chip are interconnected by neuromorphic synapses, thus enabling co-evolution of connectivity and co-processing of information of the two networks.