SOL2HY2
Solar To Hydrogen Hybrid Cycles


Energy
To demonstrate that hydrogen "green" production is possible through the exploitation of solar power.
The FCH JU strategy has identified hydrogen production by water decomposition pathways powered by renewables such as solar energy to be a major component for sustainable and carbon-free hydrogen supply. Solar-powered thermo-chemical cycles are capable to directly transfer concentrated sunlight into chemical energy by a series of chemical and electrochemical reactions, and of these cycles, hybrid-sulphur (HyS) cycle was identified as the most promising one.The challenges in HyS remain mostly in dealing with materials (electrolyser, concentrator, acid decomposer/cracker and plant components) and with the whole process flowsheet optimization, tailored to specific solar input and plant site location. With recent technology level at large-scale hydrogen production concepts hydrogen costs are unlikely to go below 3.0-3.5 €/kg. For smaller scale plant, the costs of hydrogen might be substantially higher.
The project focuses on applied, bottle-necks solving, materials research and development and demonstration of the relevant-scale key components of the solar-powered, CO2-free hybrid water splitting cycles, complemented by their advanced modeling and process simulation including conditions and site-specific technical-economical assessment optimization, quantification and benchmarking. For the short-term integration of solar-power sources with new Outotec Open Cycle will be performed. Simplified structure, extra revenues from acid sales and highly efficient co-use of the existing plants may drop hydrogen costs by about 50-75% vs. traditional process designs.

EnginSoft will provide MODAO tools and metamodelling methods in order to simulate the full process performances, including elaboration of DoE strategy, data mining and optimisation. EnginSoft will also help SME and R&D performers in modelling issues, simulation of the relevant processes and elaboration of the models. EnginSoft has also the coordination of the project.
EnginSoft S.p.A., Italy | Aalto University Foundation, Finland | DLR - German Aerospace Authority, Germany | ENEA - Agenzia per le Nuove Tecnologie, l’Energia e lo Sviluppo Economico Sostenibile, Italy | Outotec Corp., Finland | Erbicol S.A., Switzerland | Oy Woikoski AB, Finland.
Funding Scheme Collaborative Project | Call identifier FCH-JU-2012-1, SP1-JTI-FCH.2012.2.5: Thermo-electricalchemical processes with solar heat sources


36 months
June 2013 – May 2016
EnginSoft Spa
Stefano Odorizzi, Carla Baldasso
7

Some of our competences in research and technology transfer
Research project
YOGA develops a semiautomated and standardized platform targeting clinical laboratories for tissue characterization by biopsy when very little material is available.
Research project
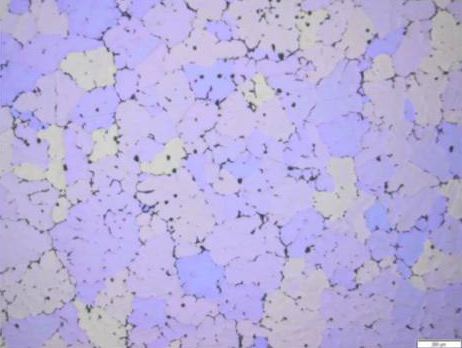
The GAP Project’s innovativeness lies in the development of innovative metallic materials with multi-sector application potential, increased by experimentation with new specific technologies (e.g. the use of ceramic cores for die-casting, surface treatments, and joining techniques).
Research project
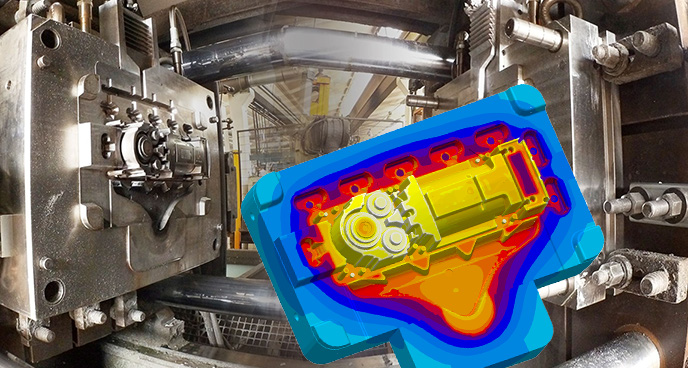
Il progetto PreMANI ambisce a dimostrare la capacità di penetrazione di tali tecniche in settori applicativi eterogenei, caratterizzati da esigenze molto diverse, facendo leva sugli aspetti metodologici di natura generale.