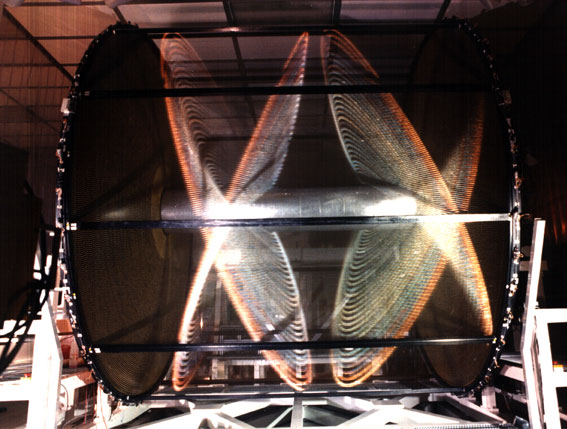
The Mu2e particle detector at FermiLAB in Chicago, Illinois
Abstract
This project, a collaboration between EnginSoft and the Italian Institute of Nuclear Physics (I.N.F.N.), involved the structural analysis and the design optimization of a Drift Chamber to be mounted on the Mu2e particle detector at FermiLAB in Chicago, Illinois. The ultimate goal of the study was to optimize the Drift Chamber’s performance in terms of stiffness, strength and weight. The nature of this project required in-depth multi-disciplinary knowledge of the best pracitices in design for prototyping as well as expertise in the choice and use of different commercial simulation packages that when used together could produce the optimal results. We were very excited when INFN acknowledged that EnginSoft’s expertise in integrated design chain solutions was a perfect match for these requirements.
The object to be simulated was a drift chamber made of composites to be manufactured by INFN and to be mounted on the Mu2e particle detector at FermiLAB. The particle detector at FermiLAB consists of a linear collider that is able to track and monitor the moving path of a stream of particles before the impact which will occur at the center of the Drift Chamber.
The collider will be employed to detect the presence of sub-atomic particles and for reconstructing their after-impact trajectories. This is done by analyzing the variation of the electric signals produced by hundreds of thousands of pre-loaded electric wires. The analysis of these signals and in particular of their energy levels, together with the study of the after-impact interations between the different particles determine the number as well as the type of such sub-atomic particles produced after the impact. The main structure of the chamber consists of an internal cyclinder enclosed by two external plates.
